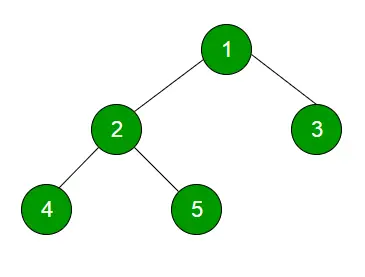
Lygio tvarka Technika apibrėžiama kaip būdas pereiti medį taip, kad visi tame pačiame lygyje esantys mazgai būtų perkeliami visiškai prieš pereinant per kitą lygį.
Pavyzdys:
Rekomenduojamo praktikos lygio užsakymo perkėlimas Išbandykite!Įvestis:
Išvestis:
1
23
Keturi
Kaip veikia lygio užsakymo apžiūra?
Pagrindinė lygio tvarkos perėjimo idėja yra pereiti visus žemesnio lygio mazgus prieš pereinant į bet kurį aukštesnio lygio mazgą. Tai galima padaryti bet kuriuo iš šių būdų:
- naivus (medžio aukščio radimas ir kiekvieno lygio perėjimas ir to lygio mazgų atspausdinimas)
- efektyviai naudojant eilę.
Lygio tvarkos perėjimas (naivus požiūris):
Rasti aukščio medžio. Tada kiekvienam lygiui paleiskite rekursinę funkciją, išlaikydami esamą aukštį. Kai mazgo lygis sutampa, atspausdinkite tą mazgą.
Toliau pateikiamas pirmiau minėto metodo įgyvendinimas:
C++ // Recursive CPP program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include using namespace std; // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child class node { public: int data; node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level); int height(node* node); node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) cout << root->duomenis<< ' '; else if (level>1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root->right, level - 1); } } // Apskaičiuokite medžio 'aukštį' – // mazgų skaičius ilgiausiu keliu nuo šaknies mazgo // žemyn iki tolimiausio lapo mazgo. int aukštis(mazgas* mazgas) { if (mazgas == NULL) return 0; else { // Apskaičiuokite kiekvieno pomedžio aukštį int lheight = aukštis(mazgas->kairė); int rheight = aukštis(mazgas->dešinė); // Naudokite didesnį if (lheight> rheight) { return (lheight + 1); } else { return (dešinėn + 1); } } } // Pagalbinė funkcija, kuri priskiria // naują mazgą su nurodytais duomenimis ir // NULL kairiąją ir dešinę rodykles. mazgas* naujasMazgas(int data) { mazgas* Mazgas = naujas mazgas(); Mazgas->duomenys = duomenys; Mazgas->kairė = NULL; Mazgas->dešinė = NULL; grįžti (Node); } // Tvarkyklės kodas int main() { mazgas* root = newMazgas(1); root->left = naujasMazgas(2); root->right = naujasMazgas(3); šaknis->kairė->kairė = naujasMazgas(4); šaknis->kairė->dešinė = newMagas(5); cout<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra> C // Recursive C program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include #include // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level); int height(struct node* node); struct node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) printf('%d ', root->duomenys); else if (level> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root->right, level - 1); } } // Apskaičiuokite medžio 'aukštį' -- // mazgų skaičius ilgiausiu keliu nuo šaknies mazgo // žemyn iki tolimiausio lapo mazgo int aukštis(struct node* node) { if (mazgas) == NULL) grąžinti 0; else { // Apskaičiuokite kiekvieno pomedžio aukštį int lheight = aukštis(mazgas->kairė); int rheight = aukštis(mazgas->dešinė); // Naudokite didesnį if (lheight> rheight) return (lheight + 1); kitaip grįžti (dešinė + 1); } } // Pagalbinė funkcija, kuri priskiria naują mazgą su // nurodytais duomenimis ir NULL kairiąja ir dešiniąja rodyklėmis. struct mazgas* naujasMazgas(int data) { struct mazgas* mazgas = (struktūros mazgas*)malloc(dydis(struktūros mazgas)); mazgas->duomenys = duomenys; mazgas->kairė = NULL; mazgas->dešinė = NULL; grįžti (mazgas); } // Tvarkyklės programa aukščiau pateiktoms funkcijoms išbandyti int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); root->left = naujasMazgas(2); root->right = naujasMazgas(3); šaknis->kairė->kairė = naujasMazgas(4); šaknis->kairė->dešinė = newMagas(5); printf('Dvejetainio medžio lygio tvarka yra
'); printLevelOrder(root); grąžinti 0; }> Java // Recursive Java program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class BinaryTree { // Root of the Binary Tree Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order traversal of tree void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number of // nodes along the longest path from the root node // down to the farthest leaf node. int height(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>dešinė) grąža (lheight + 1); kitaip grįžti (dešinė + 1); } } // Spausdinti mazgus dabartiniame lygyje void printCurrentLevel(Node root, int level) { if (root == null) return; if (lygis == 1) System.out.print(root.data + ' '); else if (level> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Tvarkyklės programa aukščiau pateiktoms funkcijoms išbandyti public static void main(String args[]) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); medis.root = naujas mazgas(1); medis.root.left = naujas mazgas(2); medis.root.right = naujas mazgas(3); medis.root.left.left = naujas mazgas(4); medis.root.left.right = naujas mazgas(5); System.out.println('Level order traversal of' + 'dvejetainis medis yra '); medis.printLevelOrder(); } }>>Python1: printCurrentLevel(root.left, level-1) printCurrentLevel(root.right, level-1) # Apskaičiuokite medžio aukštį – mazgų skaičių # ilgiausiu keliu nuo šaknies mazgo iki # tolimiausio lapo mazgas def aukštis(mazgas): jei mazgas yra None: grąžinkite 0 else: # Apskaičiuokite kiekvieno pomedžio aukštį lheight = aukštis(mazgas.kairėje) rheight = aukštis(mazgas.dešinė) # Naudokite didesnį, jei lheight> rheight: grįžti lheight+1 else: return rheight+1 # Tvarkyklės programa, kuri patikrins aukščiau pateiktą funkciją, jei __name__ == '__main__': root = Mazgas (1) root.left = Mazgas (2) root.right = Mazgas (3) šaknis. left.left = Mazgas(4) root.left.right = Mazgas(5) print('Dvejetainio medžio lygio tvarka yra -') printLevelOrder(root) # Šį kodą sukūrė Nikhilas Kumaras Singhas(nickzuck_007)> C# // Recursive c# program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree using System; // Class containing left and right // child of current node and key value public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class GFG { // Root of the Binary Tree public Node root; public void BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order // traversal of tree public virtual void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) { printCurrentLevel(root, i); } } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- // the number of nodes along the longest // path from the root node down to the // farthest leaf node. public virtual int height(Node root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>dešinė) { grįžti (aukštis + 1); } else { return (dešinėn + 1); } } } // Spausdinti mazgus dabartiniame lygyje public virtual void printCurrentLevel(Node root, int level) { if (root == null) { return; } if (level == 1) { Console.Write(root.data + ' '); } else if (level> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Tvarkyklės kodas public static void Main(string[] args) { GFG medis = new GFG(); medis.root = naujas mazgas(1); medis.root.left = naujas mazgas(2); medis.root.right = naujas mazgas(3); medis.root.left.left = naujas mazgas(4); medis.root.left.right = naujas mazgas(5); Console.WriteLine('Level order traversal ' + 'dvejetainio medžio yra '); medis.printLevelOrder(); } } // Šį kodą sukūrė Shrikant13>>Javascriptdešinė) grąža (lheight + 1); kitaip grįžti (dešinė + 1); } } // Spausdinti mazgus esamame lygyje function printCurrentLevel(root , level) { if (root == null) return; if (lygis == 1) console.log(root.data + ' '); else if (level> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Tvarkyklės programa aukščiau pateiktoms funkcijoms patikrinti root = new Node(1); root.left = naujas mazgas(2); root.right = naujas mazgas(3); root.left.left = naujas mazgas(4); root.left.right = naujas mazgas(5); console.log('Dvejetainio medžio lygio tvarka yra '); printLevelOrder(); // Šį kodą sukūrė umadevi9616>>
Išvestis Level Order traversal of binary tree is 1 2 3 4 5>
Laiko sudėtingumas: O(N), kur N yra iškreipto medžio mazgų skaičius.
Pagalbinė erdvė: O(1) Jei atsižvelgiama į rekursijos krūvą, naudojama vieta yra O(N).
abs c kodas
Lygio užsakymo perėjimas naudojant Eilė
Turime aplankyti žemesnio lygio mazgus prieš bet kurį aukštesnio lygio mazgą, ši idėja yra gana panaši į eilę. Stumkite žemesnio lygio mazgus eilėje. Kai aplankysite bet kurį mazgą, iškelkite tą mazgą iš eilės ir į eilę įstumkite to mazgo antrinį elementą.
Tai užtikrina, kad žemesnio lygio mazgas būtų aplankytas prieš bet kurį aukštesnio lygio mazgą.
Toliau pateikiamas pirmiau minėto metodo įgyvendinimas:
C++ // C++ program to print level order traversal #include using namespace std; // A Binary Tree Node struct Node { int data; struct Node *left, *right; }; // Iterative method to find height of Binary Tree void printLevelOrder(Node* root) { // Base Case if (root == NULL) return; // Create an empty queue for level order traversal queueq; // Eilės šaknis ir inicijavimo aukštis q.push(root); while (q.empty() == false) { // Spausdinti eilės priekį ir pašalinti jį iš eilės Node* node = q.front(); cout<< node->duomenis<< ' '; q.pop(); // Enqueue left child if (node->left != NULL) q.push(mazgas->left); // Eilės dešinysis vaikas if (mazgas->dešinė != NULL) q.push(mazgas->dešinė); } } // Naudingoji funkcija sukurti naują medžio mazgą Node* newNode(int data) { Node* temp = new Node; temp->duomenys = duomenys; temp->left = temp->right = NULL; grąžinimo temperatūra; } // Tvarkyklės programa aukščiau pateiktoms funkcijoms išbandyti int main() { // Sukurkime dvejetainį medį, parodytą aukščiau esančioje diagramoje Mazgas* root = newNode(1); root->left = naujasMazgas(2); root->right = naujasMazgas(3); šaknis->kairė->kairė = naujasMazgas(4); šaknis->kairė->dešinė = newMagas(5); cout<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; }> C // Iterative Queue based C program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree #include #include #define MAX_Q_SIZE 500 // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node* left; struct node* right; }; // Function prototypes struct node** createQueue(int*, int*); void enQueue(struct node**, int*, struct node*); struct node* deQueue(struct node**, int*); // Given a binary tree, print its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int rear, front; struct node** queue = createQueue(&front, &rear); struct node* temp_node = root; while (temp_node) { printf('%d ', temp_node->duomenys); // Eilės kairysis vaikas if (temp_node->left) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->left); // Eilės dešinysis vaikas if (temp_node->right) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->right); // Ištraukite mazgą į eilę ir padarykite jį temp_node temp_node = deQueue(queue, &front); } } // Naudingumo funkcijos struct node** createQueue(int* front, int* rear) { struct node** queue = (struct node**)malloc( sizeof(struct node*) * MAX_Q_SIZE); *priekyje = *galine = 0; grąžinimo eilė; } void enQueue(struktūros mazgas** eilė, int* galinis, struktūrinis mazgas* naujas_mazgas) { eilė[*galinis] = naujas_mazgas; (*galinė)++; } struct mazgas* deQueue(struct mazgas** eilė, int* priekis) { (*priekis)++; grąžinimo eilė[*priekis - 1]; } // Pagalbinė funkcija, kuri paskiria naują mazgą su nurodytais // duotais duomenimis ir NULL kairiąja ir dešiniąja rodyklėmis. struct mazgas* naujasMazgas(int data) { struct mazgas* mazgas = (struktūros mazgas*)malloc(dydis(struktūros mazgas)); mazgas->duomenys = duomenys; mazgas->kairė = NULL; mazgas->dešinė = NULL; grįžti (mazgas); } // Tvarkyklės programa aukščiau pateiktoms funkcijoms išbandyti int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); root->left = naujasMazgas(2); root->right = naujasMazgas(3); šaknis->kairė->kairė = naujasMazgas(4); šaknis->kairė->dešinė = newMagas(5); printf('Dvejetainio medžio lygio tvarka yra
'); printLevelOrder(root); grąžinti 0; }> Java // Iterative Queue based Java program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; // Class to represent Tree node class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queueeilė = naujas LinkedList(); queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // poll() pašalina esamą antraštę. Mazgas tempMazgas = queue.poll(); System.out.print(tempNode.data + ' '); // Eilės kairysis vaikas if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.add(tempNode.left); } // Eilės dešinysis antrinis if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.add(tempNode.right); } } } public static void main(String args[]) { // Dvejetainio medžio kūrimas ir // mazgų įvedimas BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree(); tree_level.root = naujas mazgas(1); tree_level.root.left = naujas mazgas(2); tree_level.root.right = naujas mazgas(3); tree_level.root.left.left = naujas mazgas(4); tree_level.root.left.right = naujas mazgas(5); System.out.println('Dvejetainio medžio lygio tvarka yra - '); tree_level.printLevelOrder(); } }>>Python> C#> Javascript Išvestis
Pagalbinė erdvė: O(N) čia N yra mazgų skaičius dvejetainiame medyje.