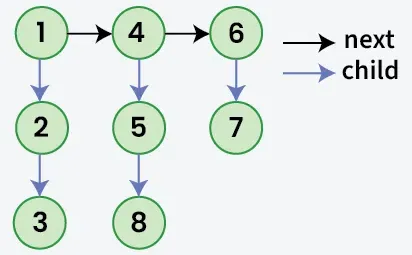
Pateiktas susietas sąrašas, kuriame, be kitas kiekvienas mazgas turi a vaikas žymeklį, kuris gali nukreipti arba nenurodyti į atskirą sąrašą. Šie vaikų sąrašai gali turėti vieną ar daugiau savo vaikams gaminti a daugiapakopis susietas sąrašas. Atsižvelgiant į galva iš pirmas lygis sąrašo. Užduotis yra išlyginti sąrašą, kad visi mazgai būtų rodomi a vieno lygio susietas sąrašas. Išlyginkite sąrašą taip, kad visi mazgai pirmas lygis turėtų ateiti pirma tada mazgai antra lygis ir pan.
Pavyzdžiai:
Įvestis:
java eilutė
šaukštelis vs šaukštasIšvestis: 1->4->6->2->5->7->3->8
Paaiškinimas: Daugiapakopis susietas sąrašas yra išlygintas, nes jame nėra antrinių nuorodų.
Mes aptarėme kelių lygių susieto sąrašo išlyginimas kur mazgai turi dvi rodykles žemyn ir toliau. Ankstesniame įraše mes suplota susietą sąrašą lygiai išmintingai. Kaip išlyginti susietą sąrašą, kai visada turime apdoroti rodyklė žemyn prieš kitą kiekviename mazge.
Turinio lentelė
- [Numatomas požiūris] Naudojant rekursiją – O(n) laikas ir O(n) erdvė
- [Alternatyvus metodas] Naudojant krūvą – O(n) laikas ir O(n) erdvė
[Numatomas požiūris] Naudojant rekursiją – O(n) laikas ir O(n) erdvė
C++Metodas yra rekursyviai išlyginti a kelių lygių susietas sąrašą pereinant kiekvieną mazgą ir jo antrinius mazgus. Pirma išlyginkite vaikų sąrašą naudojant rekursiją. Kai vaikų sąrašas bus išlygintas, pereikite prie kitas mazgas eilėje. Važiavimo metu palaikykite a nuoroda prie anksčiau aplankytas mazgas ir susieti jį su dabartiniu mazgu. Šis procesas užtikrina, kad visi skirtingų lygių mazgai būtų sujungti a vienas linijinis sąrašas išsaugant gylio tvarka.
25 c iki k
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise #include
// A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { int data; Node next down; Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void flattenList(Node curr Node[] prev) { if (curr == null) return; // Add the current element to the list. if (prev[0] != null) prev[0].next = curr; prev[0] = curr; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr.next; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList(curr.down prev); // Recursively add the next list flattenList(next prev); } static void printList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { System.out.print(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); Node[] prev = new Node[1]; flattenList(head prev); printList(head); } }
# A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.next = None self.down = None def flatten_list(curr prev): if curr is None: return # Add the current element to the list. if prev[0] is not None: prev[0].next = curr prev[0] = curr # Store the next pointer next_node = curr.next # Recursively add the bottom list flatten_list(curr.down prev) # Recursively add the next list flatten_list(next_node prev) def print_list(head): curr = head while curr is not None: print(curr.data end=' ') curr = curr.next print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node(5) head.down = Node(7) head.down.down = Node(8) head.down.down.down = Node(30) head.next = Node(10) head.next.next = Node(19) head.next.next.down = Node(22) head.next.next.down.down = Node(50) head.next.next.next = Node(28) prev = [None] flatten_list(head prev) print_list(head)
// A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using System; class Node { public int data; public Node next down; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList(Node curr ref Node prev) { if (curr == null) return; // Add the current element to the list. if (prev != null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr.next; // Recursively add the bottom list FlattenList(curr.down ref prev); // Recursively add the next list FlattenList(next ref prev); } static void PrintList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Console.Write(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); Node prev = null; FlattenList(head ref prev); PrintList(head); } }
// A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; this.down = null; } } function flattenList(curr prev) { if (curr === null) return; // Add the current element to the list. if (prev[0] !== null) prev[0].next = curr; prev[0] = curr; // Store the next pointer let next = curr.next; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList(curr.down prev); // Recursively add the next list flattenList(next prev); } function printList(head) { let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { console.log(curr.data); curr = curr.next; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); let prev = [null]; flattenList(head prev); printList(head);
Išvestis
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28
[Alternatyvus metodas] Naudojant krūvą – O(n) laikas ir O(n) erdvė
C++Metodas yra kirsti kelių lygių susietas sąrašas naudojant a krūva . Pradėkite nuo stumdymas į galvos mazgas ant kamino. Tada, kol krūva nėra tuščia pop viršutinį mazgą ir jį apdoroti. Kiekvienam mazgui stumti jos kitos ir žemyn nukreiptos rodyklės (jei jie yra) ant kamino. Šio proceso metu susieti dabartinį mazgą su ankstesniu mazgu išlaikant sąrašą suplokšta forma. Perėjimas užtikrina, kad visų lygių mazgai būtų sujungti a vieno lygio susietas sąrašas išsaugant gylio tvarką.
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack #include
// A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack import java.util.Stack; class Node { int data; Node next down; Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void flattenList(Node head) { if (head == null) return; Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(head); Node prev = null; while (!stack.isEmpty()) { Node curr = stack.pop(); // Push the next node first if (curr.next != null) stack.push(curr.next); // Push the bottom node into stack if (curr.down != null) stack.push(curr.down); // Add the current element to the list if (prev != null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; } } static void printList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { System.out.print(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); flattenList(head); printList(head); } }
# A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise using stack class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.next = None self.down = None def flatten_list(head): if head is None: return stack = [head] prev = None while stack: curr = stack.pop() # Push the next node first if curr.next: stack.append(curr.next) # Push the bottom node into stack if curr.down: stack.append(curr.down) # Add the current element to the list if prev: prev.next = curr prev = curr def print_list(head): curr = head while curr: print(curr.data end=' ') curr = curr.next print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node(5) head.down = Node(7) head.down.down = Node(8) head.down.down.down = Node(30) head.next = Node(10) head.next.next = Node(19) head.next.next.down = Node(22) head.next.next.down.down = Node(50) head.next.next.next = Node(28) flatten_list(head) print_list(head)
// A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node next down; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList(Node head) { if (head == null) return; Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); stack.Push(head); Node prev = null; while (stack.Count > 0) { Node curr = stack.Pop(); // Push the next node first if (curr.next != null) stack.Push(curr.next); // Push the bottom node into stack if (curr.down != null) stack.Push(curr.down); // Add the current element to the list if (prev != null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; } } static void PrintList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Console.Write(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); FlattenList(head); PrintList(head); } }
// A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; this.down = null; } } function flattenList(head) { if (head === null) return; let stack = [head]; let prev = null; while (stack.length > 0) { let curr = stack.pop(); // Push the next node first if (curr.next !== null) stack.push(curr.next); // Push the bottom node into stack if (curr.down !== null) stack.push(curr.down); // Add the current element to the list if (prev !== null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; } } function printList(head) { let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { console.log(curr.data); curr = curr.next; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); flattenList(head); printList(head);
Išvestis
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28