Euklido algoritmas yra būdas rasti didžiausią bendrą dviejų teigiamų sveikųjų skaičių daliklį. Dviejų skaičių GCD yra didžiausias skaičius, dalijantis juos abu. Paprastas būdas rasti GCD – padalyti skaičius ir padauginti bendruosius pirminius veiksnius.
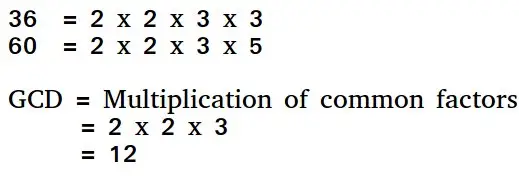
Pagrindinis Euklido algoritmas GCD:
Algoritmas pagrįstas toliau pateiktais faktais.
- Jei iš didesnio atimame mažesnį skaičių (didesnį skaičių sumažiname), GCD nesikeičia. Taigi, jei nuolat atimame didesnį iš dviejų, gauname GCD.
- Dabar vietoj atimties, jei padaliname mažesnį skaičių, algoritmas sustoja, kai randame likutį 0.
Žemiau yra rekursinė funkcija, skirta įvertinti gcd naudojant Euklido algoritmą:
C
// C program to demonstrate Basic Euclidean Algorithm> #include> // Function to return gcd of a and b> int> gcd(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >if> (a == 0)> >return> b;> >return> gcd(b % a, a);> }> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >int> a = 10, b = 15;> > >// Function call> >printf>(>'GCD(%d, %d) = %d
'>, a, b, gcd(a, b));> >a = 35, b = 10;> >printf>(>'GCD(%d, %d) = %d
'>, a, b, gcd(a, b));> >a = 31, b = 2;> >printf>(>'GCD(%d, %d) = %d
'>, a, b, gcd(a, b));> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
CPP
// C++ program to demonstrate> // Basic Euclidean Algorithm> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Function to return> // gcd of a and b> int> gcd(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >if> (a == 0)> >return> b;> >return> gcd(b % a, a);> }> // Driver Code> int> main()> {> >int> a = 10, b = 15;> > >// Function call> >cout <<>'GCD('> << a <<>', '> << b <<>') = '> << gcd(a, b)> ><< endl;> >a = 35, b = 10;> >cout <<>'GCD('> << a <<>', '> << b <<>') = '> << gcd(a, b)> ><< endl;> >a = 31, b = 2;> >cout <<>'GCD('> << a <<>', '> << b <<>') = '> << gcd(a, b)> ><< endl;> >return> 0;> }> |
>
romėniškų skaitmenų diagrama 1100
>
Java
// Java program to demonstrate Basic Euclidean Algorithm> import> java.lang.*;> import> java.util.*;> class> GFG {> >// extended Euclidean Algorithm> >public> static> int> gcd(>int> a,>int> b)> >{> >if> (a ==>0>)> >return> b;> >return> gcd(b % a, a);> >}> >// Driver code> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >int> a =>10>, b =>15>, g;> > >// Function call> >g = gcd(a, b);> >System.out.println(>'GCD('> + a +>' , '> + b> >+>') = '> + g);> >a =>35>;> >b =>10>;> >g = gcd(a, b);> >System.out.println(>'GCD('> + a +>' , '> + b> >+>') = '> + g);> >a =>31>;> >b =>2>;> >g = gcd(a, b);> >System.out.println(>'GCD('> + a +>' , '> + b> >+>') = '> + g);> >}> }> // Code Contributed by Mohit Gupta_OMG> |
>
>
Python3
# Python3 program to demonstrate Basic Euclidean Algorithm> # Function to return gcd of a and b> def> gcd(a, b):> >if> a>=>=> 0>:> >return> b> >return> gcd(b>%> a, a)> # Driver code> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> >a>=> 10> >b>=> 15> >print>(>'gcd('>, a,>','>, b,>') = '>, gcd(a, b))> >a>=> 35> >b>=> 10> >print>(>'gcd('>, a,>','>, b,>') = '>, gcd(a, b))> >a>=> 31> >b>=> 2> >print>(>'gcd('>, a,>','>, b,>') = '>, gcd(a, b))> # Code Contributed By Mohit Gupta_OMG> |
>
>
C#
// C# program to demonstrate Basic Euclidean Algorithm> using> System;> class> GFG {> >public> static> int> gcd(>int> a,>int> b)> >{> >if> (a == 0)> >return> b;> >return> gcd(b % a, a);> >}> >// Driver Code> >static> public> void> Main()> >{> >int> a = 10, b = 15, g;> >g = gcd(a, b);> >Console.WriteLine(>'GCD('> + a +>' , '> + b> >+>') = '> + g);> >a = 35;> >b = 10;> >g = gcd(a, b);> >Console.WriteLine(>'GCD('> + a +>' , '> + b> >+>') = '> + g);> >a = 31;> >b = 2;> >g = gcd(a, b);> >Console.WriteLine(>'GCD('> + a +>' , '> + b> >+>') = '> + g);> >}> }> // This code is contributed by ajit> |
>
>
PHP
// php program to demonstrate Basic Euclidean Algorithm> // PHP program to demonstrate // Basic Euclidean Algorithm // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd($a, $b) { if ($a == 0) return $b; return gcd($b % $a, $a); } // Driver Code $a = 10; $b = 15; // Function call echo 'GCD(',$a,',' , $b,') = ', gcd($a, $b); echo '
'; $a = 35; $b = 10; echo 'GCD(',$a ,',',$b,') = ', gcd($a, $b); echo '
'; $a = 31; $b = 2; echo 'GCD(',$a ,',', $b,') = ', gcd($a, $b); // This code is contributed by m_kit ?>>> |
>
// JavaScript program to demonstrate>// Basic Euclidean Algorithm>// Function to return>// gcd of a and b>function>gcd( a, b)>{>>if>(a == 0)>>return>b;>>return>gcd(b % a, a);>}>// Driver Code>>let a = 10, b = 15;>>document.write(>'GCD('>+ a +>', '>>+ b +>') = '>+ gcd(a, b) +>' '>);>>>a = 35, b = 10;>>document.write(>'GCD('>+ a +>', '>>+ b +>') = '>+ gcd(a, b) +>' '>);>>>a = 31, b = 2;>>document.write(>'GCD('>+ a +>', '>>+ b +>') = '>+ gcd(a, b) +>' '>);>// This code contributed by aashish1995>>dvejetainis medis inorder traversal>IšvestisGCD(10, 15) = 5 GCD(35, 10) = 5 GCD(31, 2) = 1>Laiko sudėtingumas: O (min. žurnalo (a, b))
Pagalbinė erdvė: O(Žurnalas (min(a,b))Išplėstinis euklido algoritmas:
Išplėstinis Euklido algoritmas taip pat randa sveikųjų skaičių koeficientus x ir y, kad: ax + by = gcd(a, b)
Pavyzdžiai:
Įvestis: a = 30, b = 20
Išvestis: gcd = 10, x = 1, y = -1
(Atkreipkite dėmesį, kad 30*1 + 20*(-1) = 10)Įvestis: a = 35, b = 15
Išvestis: gcd = 5, x = 1, y = -2
(Atkreipkite dėmesį, kad 35*1 + 15*(-2) = 5)Išplėstinis Euklido algoritmas atnaujina gcd(a, b) rezultatus, naudodamas rezultatus, apskaičiuotus rekursiniu skambučiu gcd(b%a, a). Tegul x ir y reikšmės, apskaičiuotos rekursiniu skambučiu, yra x1ir y1. x ir y atnaujinami naudojant toliau pateiktas išraiškas.
Rekomenduojamos praktikos išplėstinis euklido algoritmas Išbandykite!ax + by = gcd(a, b)
gcd(a, b) = gcd(b%a, a)
gcd(b%a, a) = (b%a)x1+ yra1
ax + by = (b%a)x1+ yra1
ax + by = (b – [b/a] * a)x1+ yra1
ax + by = a(y1– [b/a] * x1) + bx1Lyginant LHS ir RHS,
x = y1– ?b/a? *x1
y = x1Žemiau pateikiamas pirmiau minėto metodo įgyvendinimas:
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate working of>// extended Euclidean Algorithm>#include>using>namespace>std;>// Function for extended Euclidean Algorithm>int>gcdExtended(>int>a,>int>b,>int>*x,>int>*y)>{>>// Base Case>>if>(a == 0)>>{>>*x = 0;>>*y = 1;>>return>b;>>}>>int>x1, y1;>// To store results of recursive call>>int>gcd = gcdExtended(b%a, a, &x1, &y1);>>// Update x and y using results of>>// recursive call>>*x = y1 - (b/a) * x1;>>*y = x1;>>return>gcd;>}>// Driver Code>int>main()>{>>int>x, y, a = 35, b = 15;>>int>g = gcdExtended(a, b, &x, &y);>>cout <<>'GCD('><< a <<>', '><< b>><<>') = '><< g << endl;>>return>0;>}>>>C
// C program to demonstrate working of extended>// Euclidean Algorithm>#include>// C function for extended Euclidean Algorithm>int>gcdExtended(>int>a,>int>b,>int>*x,>int>*y)>{>>// Base Case>>if>(a == 0)>>{>>*x = 0;>>*y = 1;>>return>b;>>}>>int>x1, y1;>// To store results of recursive call>>int>gcd = gcdExtended(b%a, a, &x1, &y1);>>// Update x and y using results of recursive>>// call>>*x = y1 - (b/a) * x1;>>*y = x1;>>return>gcd;>}>// Driver Program>int>main()>{>>int>x, y;>>int>a = 35, b = 15;>>int>g = gcdExtended(a, b, &x, &y);>>printf>(>'gcd(%d, %d) = %d'>, a, b, g);>>return>0;>}>>>Java
// Java program to demonstrate working of extended>// Euclidean Algorithm>import>java.lang.*;>import>java.util.*;>class>GFG {>>// extended Euclidean Algorithm>>public>static>int>gcdExtended(>int>a,>int>b,>int>x,>>int>y)>>{>>// Base Case>>if>(a ==>0>) {>>x =>0>;>>y =>1>;>>return>b;>>}>>int>x1 =>1>,>>y1 =>1>;>// To store results of recursive call>>int>gcd = gcdExtended(b % a, a, x1, y1);>>// Update x and y using results of recursive>>// call>>x = y1 - (b / a) * x1;>>y = x1;>>return>gcd;>>}>>// Driver Program>>public>static>void>main(String[] args)>>{>>int>x =>1>, y =>1>;>>int>a =>35>, b =>15>;>>int>g = gcdExtended(a, b, x, y);>>System.out.print(>'gcd('>+ a +>' , '>+ b>>+>') = '>+ g);>>}>}>>alter pridėti stulpelį orakulas>Python3
# Python program to demonstrate working of extended># Euclidean Algorithm># function for extended Euclidean Algorithm>def>gcdExtended(a, b):>># Base Case>>if>a>=>=>0>:>>return>b,>0>,>1>>gcd, x1, y1>=>gcdExtended(b>%>a, a)>># Update x and y using results of recursive>># call>>x>=>y1>->(b>/>/>a)>*>x1>>y>=>x1>>return>gcd, x, y># Driver code>a, b>=>35>,>15>g, x, y>=>gcdExtended(a, b)>print>(>'gcd('>, a,>','>, b,>') = '>, g)>>>C#
// C# program to demonstrate working>// of extended Euclidean Algorithm>using>System;>class>GFG>{>>>// extended Euclidean Algorithm>>public>static>int>gcdExtended(>int>a,>int>b,>>int>x,>int>y)>>{>>// Base Case>>if>(a == 0)>>{>>x = 0;>>y = 1;>>return>b;>>}>>// To store results of>>// recursive call>>int>x1 = 1, y1 = 1;>>int>gcd = gcdExtended(b % a, a, x1, y1);>>// Update x and y using>>// results of recursive call>>x = y1 - (b / a) * x1;>>y = x1;>>return>gcd;>>}>>>// Driver Code>>static>public>void>Main ()>>{>>int>x = 1, y = 1;>>int>a = 35, b = 15;>>int>g = gcdExtended(a, b, x, y);>>Console.WriteLine(>'gcd('>+ a +>' , '>+>>b +>') = '>+ g);>>}>}>>>PHP
// PHP program to demonstrate // working of extended // Euclidean Algorithm // PHP function for // extended Euclidean // Algorithm function gcdExtended($a, $b, $x, $y) { // Base Case if ($a == 0) { $x = 0; $y = 1; return $b; } // To store results // of recursive call $gcd = gcdExtended($b % $a, $a, $x, $y); // Update x and y using // results of recursive // call $x = $y - floor($b / $a) * $x; $y = $x; return $gcd; } // Driver Code $x = 0; $y = 0; $a = 35; $b = 15; $g = gcdExtended($a, $b, $x, $y); echo 'gcd(',$a; echo ', ' , $b, ')'; echo ' = ' , $g; ?>>>>
>// Javascript program to demonstrate>// working of extended>// Euclidean Algorithm>// Javascript function for>// extended Euclidean>// Algorithm>function>gcdExtended(a, b,>>x, y)>{>>// Base Case>>if>(a == 0)>>{>>x = 0;>>y = 1;>>return>b;>>}>>// To store results>>// of recursive call>>let gcd = gcdExtended(b % a,>>a, x, y);>>// Update x and y using>>// results of recursive>>// call>>x = y - (b / a) * x;>>y = x;>>return>gcd;>}>// Driver Code>let x = 0;>let y = 0;>let a = 35;>let b = 15;>let g = gcdExtended(a, b, x, y);>document.write(>'gcd('>+ a);>document.write(>', '>+ b +>')'>);>document.write(>' = '>+ g);>>>>Išvestis:
gcd(35, 15) = 5>Laiko sudėtingumas: O(log N)
Pagalbinė erdvė: O(log N)Kaip veikia išplėstinis algoritmas?
Kaip matyti aukščiau, x ir y yra įvesties a ir b rezultatai,
a.x + b.y = gcd —-(1)
Ir x1ir y1yra įvesties b%a ir a rezultatai
(b%a).x1+ a.y1= gcd
Kai aukščiau įdedame b%a = (b – (?b/a?).a),
mes sekame. Atkreipkite dėmesį, kad ?b/a? yra aukštas (b/a)(b – (?b/a?).a).x1+ a.y1= gcd
Aukščiau pateiktą lygtį taip pat galima parašyti taip, kaip nurodyta toliau
b.x1+ a.(ir1– (?b/a?).x1) = gcd — (2)
Palyginę „a“ ir „b“ koeficientus (1) ir
(2), gauname taip,
x = y1– ?b/a? *x1
y = x1Kuo naudingas išplėstinis algoritmas?
Išplėstinis Euklido algoritmas yra ypač naudingas, kai a ir b yra pirminiai (arba gcd yra 1). Kadangi x yra modulinis dauginamasis atvirkštinis modulis b, o y yra modulinis dauginamasis atvirkštinis modulis modulis a. Visų pirma, modulinio multiplikacinio atvirkštinio skaičiavimas yra esminis RSA viešojo rakto šifravimo metodo žingsnis.
