Atsižvelgiant į atskirai susietą sąrašą, užduotis yra ištrinti vidurinį sąrašo mazgą.
- Jei sąraše yra lygus mazgų skaičius, bus du viduriniai mazgai. Tokiu atveju ištrinkite antrąjį vidurinį mazgą.
- Jei susietą sąrašą sudaro tik vienas mazgas, grąžinkite NULL.
Pavyzdys:
Įvestis: „LinkedList“: 1-> 2-> 3-> 4-> 5
Išvestis: 1-> 2-> 4-> 5
Paaiškinimas:
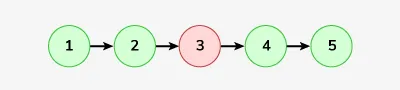
Įvestis: „LinkedList“: 2-> 4-> 6-> 7-> 5-> 1
Išvestis: 2-> 4-> 6-> 5-> 1
Paaiškinimas: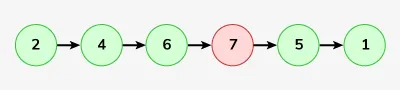
Įvestis: „LinkedList“: 7
Išvestis:
Turinio lentelė
]
Pagrindinė šio požiūrio idėja yra pirmiausia peržengti visą susietą sąrašą, kad būtų suskaičiuotas bendras mazgų skaičius. Sužinoję bendrą mazgų skaičių, galime apskaičiuoti vidurinio mazgo padėtį, esančią rodyklėje N/2 (kur n yra bendras mazgų skaičius). Tada dar kartą eikite per susietą sąrašą, bet šį kartą sustojame tiesiai prieš vidurinį mazgą. Kai ten pakeisime kitą mazgo rodyklę prieš vidurinį mazgą, kad jis praleistų per vidurinį mazgą ir nukreiptų tiesiai į mazgą po jo
Žemiau yra aukščiau pateikto požiūrio įgyvendinimas:
C++// C++ program to delete middle of a linked list #include
// C program to delete middle of a linked list #include
// Java program to delete middle of a linked list class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } public class GfG { // Function to delete middle node from linked list. public static Node deleteMid(Node head) { // Edge case: return null if there is only // one node. if (head.next == null) return null; int count = 0; Node p1 = head p2 = head; // First pass count the number of nodes // in the linked list using 'p1'. while (p1 != null) { count++; p1 = p1.next; } // Get the index of the node to be deleted. int middleIndex = count / 2; // Second pass let 'p2' move toward predecessor // of the middle node. for (int i = 0; i < middleIndex - 1; ++i) p2 = p2.next; // Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2.next = p2.next.next; return head; } public static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { System.out.print(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } System.out.println('null'); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); System.out.print('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid(head); System.out.print ('Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head); } }
# Python3 program to delete middle of a linked list class Node: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.next = None # Function to delete middle node from linked list. def deleteMid(head): # Edge case: return None if there is only # one node. if head.next is None: return None count = 0 p1 = head p2 = head # First pass count the number of nodes # in the linked list using 'p1'. while p1 is not None: count += 1 p1 = p1.next # Get the index of the node to be deleted. middleIndex = count // 2 # Second pass let 'p2' move toward the predecessor # of the middle node. for i in range(middleIndex - 1): p2 = p2.next # Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2.next = p2.next.next return head def printList(head): temp = head while temp is not None: print(temp.data end=' -> ') temp = temp.next print('None') if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a static hardcoded linked list: # 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) print('Original Linked List:' end=' ') printList(head) # Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid(head) print('Linked List after deleting the middle node:' end=' ') printList(head)
// C# program to delete middle of a linked list using System; class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to delete middle node from linked list. static Node deleteMid(Node head) { // Edge case: return null if there is only // one node. if (head.next == null) return null; int count = 0; Node p1 = head p2 = head; // First pass count the number of nodes // in the linked list using 'p1'. while (p1 != null) { count++; p1 = p1.next; } // Get the index of the node to be deleted. int middleIndex = count / 2; // Second pass let 'p2' move toward the predecessor // of the middle node. for (int i = 0; i < middleIndex - 1; ++i) p2 = p2.next; // Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2.next = p2.next.next; return head; } static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { Console.Write(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } Console.WriteLine('null'); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); Console.Write('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid(head); Console.Write ('Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head); } }
class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } } // Function to delete middle node from linked list. function deleteMid(head) { // Edge case: return null if there is only // one node. if (head.next === null) return null; let count = 0; let p1 = head p2 = head; // First pass count the number of nodes // in the linked list using 'p1'. while (p1 !== null) { count++; p1 = p1.next; } // Get the index of the node to be deleted. let middleIndex = Math.floor(count / 2); // Second pass let 'p2' move toward the predecessor // of the middle node. for (let i = 0; i < middleIndex - 1; ++i) p2 = p2.next; // Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2.next = p2.next.next; return head; } function printList(head) { let temp = head; while (temp !== null) { console.log(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } console.log('null'); } // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); console.log('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid(head); console.log('Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head);
Išvestis
Original Linked List: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> nullptr Linked List after deleting the middle node: 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5 -> nullptr
Laiko sudėtingumas: O (n). Reikia dviejų susieto sąrašo kelionių
Pagalbinė erdvė: O (1). Nereikia jokios papildomos vietos.
[Tikimas
Aukščiau pateiktam sprendimui reikia dviejų susieto sąrašo apvažiavimų. Vidurinį mazgą galima ištrinti naudojant vieną pervažiavimą. Idėja yra naudoti du rodykles Slow_ptr ir „Fast_ptr“ . Greitas rodyklė vienu metu judina du mazgus, o lėtas rodyklė vienu metu juda vieną mazgą. Kai greitasis rodyklė pasieks sąrašo galą, lėtas rodyklė bus išdėstyta viduriniame mazge. Toliau turite prijungti mazgą, kuris yra prieš vidurinį mazgą ( Ankstesnis ) į mazgą, kuris ateina po vidurinio mazgo. Tai veiksmingai praleidžia per vidurinį mazgą, pašalindamas jį iš sąrašo.
Žemiau yra aukščiau pateikto požiūrio įgyvendinimas
C++// C++ program to delete middle of a linked list #include
// C program to delete middle of a linked list #include
// Java program to delete the middle of a linked list class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to delete middle node from linked list static Node deleteMid(Node head) { // If the list is empty return null if (head == null) return null; // If the list has only one node // delete it and return null if (head.next == null) { return null; } Node prev = null; Node slow_ptr = head; Node fast_ptr = head; // Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead // and the slow pointer 1 node ahead // until fast pointer reaches end of list while (fast_ptr != null && fast_ptr.next != null) { fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next.next; // Update prev to hold the previous // slow pointer value prev = slow_ptr; slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next; } // At this pointslow_ptr points to middle node // Bypass the middle node prev.next = slow_ptr.next; // Return the head of the modified list return head; } static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { System.out.print(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } System.out.println('NULL'); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); System.out.print('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node head = deleteMid(head); System.out.print ('Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head); } }
# Python program to delete the middle of a linked list class Node: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.next = None # Function to delete middle node from linked list def deleteMid(head): # If the list is empty return None if head is None: return None # If the list has only one node # delete it and return None if head.next is None: return None prev = None slow_ptr = head fast_ptr = head # Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead # and the slow pointer 1 node ahead # until fast pointer reaches end of the list while fast_ptr is not None and fast_ptr.next is not None: fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next.next # Update prev to hold the previous # slow pointer value prev = slow_ptr slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next # At this point slow_ptr points to middle node # Bypass the middle node prev.next = slow_ptr.next # Return the head of the modified list return head def printList(head): temp = head while temp: print(temp.data end=' -> ') temp = temp.next print('NULL') if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a static hardcoded linked list: # 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) print('Original Linked List: ' end='') printList(head) # Delete the middle node head = deleteMid(head) print('Linked List after deleting the middle node: ' end='') printList(head)
// C# program to delete middle of a linked list using System; class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to delete middle node from linked list public static Node deleteMid(Node head) { // If the list is empty return null if (head == null) return null; // If the list has only one node // delete it and return null if (head.next == null) { return null; } Node prev = null; Node slow_ptr = head; Node fast_ptr = head; // Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead // and the slow pointer 1 node ahead // until fast pointer reaches end of the list while (fast_ptr != null && fast_ptr.next != null) { fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next.next; // Update prev to hold the previous // slow pointer value prev = slow_ptr; slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next; } // At this point slow_ptr points to middle node // Bypass the middle node prev.next = slow_ptr.next; // Return the head of the modified list return head; } // Function to print the linked list public static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { Console.Write(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } Console.WriteLine('NULL'); } public static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); Console.Write('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node head = deleteMid(head); Console.Write ('Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head); } }
// javascript program to delete middle of a linked list class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } } // Function to delete the middle node from the linked list function deleteMid(head) { // If the list is empty return null if (head === null) { return null; } // If the list has only one node delete it and return // null if (head.next === null) { return null; } let prev = null; let slow_ptr = head; let fast_ptr = head; // Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead // and the slow pointer 1 node ahead // until the fast pointer reaches the end of the list while (fast_ptr !== null && fast_ptr.next !== null) { fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next.next; // Update prev to hold the previous slow pointer // value prev = slow_ptr; slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next; } // At this point slow_ptr points to the middle node // Bypass the middle node prev.next = slow_ptr.next; // Return the head of the modified list return head; } function printList(head) { let temp = head; while (temp !== null) { process.stdout.write(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } console.log('null'); } // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); process.stdout.write('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node head = deleteMid(head); process.stdout.write( 'Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head);
Išvestis
Original Linked List: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL Linked List after deleting the middle node: 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL
Laiko sudėtingumas: O (n). Reikia tik vieno susieto sąrašo pervažiavimo
Pagalbinė erdvė: O (1). Nes nereikia jokios papildomos vietos.
Susijęs straipsnis:
- Raskite susieto sąrašo vidurį


