Duotas stačiakampis matmenų popierius a x b . Užduotis yra iškirpti visą popierių į minimumas skaičius kvadratas gabalus. Galime pasirinkti bet kokio dydžio kvadratinius gabalus, tačiau jie turi būti supjaustyti nesutampa ir nepalieka papildomos vietos .
Pavyzdžiai:
Įvestis: a = 5 b = 8
5 kvadratai, iškirpti iš 5 x 8 dydžio popieriaus
Išvestis: 5
Paaiškinimas: Popierių galime supjaustyti į 5 kvadratus: 1 kvadratas 5x5 dydžio 1 kvadratas 3x3 1 kvadratas 2x2 dydžio ir 2 1x1 dydžio kvadratai.java parseintĮvestis: a = 13 b = 11
6 kvadratai, iškirpti iš 13 x 11 dydžio popieriaus
Išvestis: 6
Paaiškinimas: Popierių galime supjaustyti į 6 kvadratus: 1 kvadratas 7x7 dydžio 1 kvadratas 6x6 dydžio 1 kvadratas 5x5 dydžio 2 kvadratas 4x4 ir 1 kvadratas 1x1 dydžio.Įvestis: a = 6 b = 7
5 kvadratai, iškirpti iš 6 x 7 dydžio popieriaus
Išvestis: 5
Paaiškinimas: Popierių galime supjaustyti į 5 kvadratus: 1 kvadratas 4x4 dydžio 2 kvadratas 3x3 dydžio ir 2 3x3 dydžio kvadratai.Pete'o Davidsono pilietybė
Turinio lentelė
- [Neteisingas 1 metodas] Naudojamas godus metodas
- [Neteisingas požiūris 2] Dinaminio programavimo naudojimas
- [Teisingas požiūris] DFS ir dinaminio programavimo naudojimas
[Neteisingas 1 metodas] Naudojamas godus metodas
Iš pirmo žvilgsnio gali atrodyti, kad problemą galima nesunkiai išspręsti iš popieriaus išpjaunant didžiausią įmanomą kvadratą, po to išpjaunant didžiausią kvadratą iš likusio popieriaus ir taip toliau, kol išpjauname visą popierių. Tačiau šis sprendimas yra neteisingas.
Kodėl Greedy Approach neveiks?
Apsvarstykite dydžio popierių 6x7 tada jei bandysime godžiai karpyti popierių, gausime 7 kvadratai: 1 kvadrato dydžio 6x6 ir 6 kvadratų dydžio 1x1 kadangi teisingas sprendimas yra: 5. Todėl godus požiūris neveiks.
js kelių eilučių eilutę
[Neteisingas požiūris 2] Dinaminio programavimo naudojimas
Dinaminis programavimas su vertikaliais arba horizontaliais pjūviais: Kitas sprendimas, kuris gali atrodyti teisingas, yra naudoti Dinaminis programavimas . Galime palaikyti tokią dp[][] lentelę dp[i][j] = minimalus kvadratų, kuriuos galima iškirpti iš tokio dydžio popieriaus, skaičius i x j . Tada dėl dydžio popieriaus axb
- Galime pabandyti iškirpti išilgai kiekvienos eilutės: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) kur k gali būti diapazone [1 i - 1].
- Galime pabandyti iškirpti išilgai kiekvieno stulpelio: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i][j - k] + dp[i][k]) kur k gali būti diapazone [1 j - 1].
Galiausiai atsakymas bus minimalus visų pjūvių skaičius. Tačiau šis sprendimas taip pat neteisingas.
Kodėl pjovimas vertikaliai arba horizontaliai naudojant dinaminio programavimo metodą neveiks?
importo antTai neveiks, nes darome prielaidą, kad vertikalus arba horizontalus pjūvis visada padalins stačiakampį į dvi dalis. Apsvarstykite dydžio popierių 13x11 tada, jei bandysime iškirpti popierių naudodami DP metodą, gausime 8 kvadratus, bet teisingas atsakymas (kaip parodyta pavyzdžiuose) yra 6. Taigi dinaminis programavimas neveiks.
[Teisingas požiūris] DFS ir dinaminio programavimo naudojimas
C++The idėja yra iškirpti visą popierių naudojant DFS in iš apačios į viršų būdu. Kiekviename žingsnyje raskite apatinį kairįjį popieriaus kampą ir pabandykite iš to kampo iškirpti įvairaus dydžio kvadratus. Iškirpę kvadratą dar kartą suraskite apatinį kairįjį likusio popieriaus kampą, kad iškirptumėte visų galimų dydžių kvadratus ir pan. Bet jei bandytume iškirpti visus įmanomus kiekvieno įmanomo popieriaus dydžio apatiniame kairiajame kampe, tai būtų gana neefektyvu. Mes galime jį optimizuoti naudodami Dinaminis programavimas išsaugoti minimalius kiekvieno galimo popieriaus dydžio pjūvius.
Norėdami vienareikšmiškai identifikuoti bet kokį popieriaus dydį, galime išlaikyti remSq[] masyvą, kad remSq[i] išsaugotų likusių 1x1 dydžio kvadratų skaičių i-ajame popieriaus stulpelyje. Taigi popieriui, kurio dydis 6x7 remSq[] = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. Taip pat norėdami rasti žemiausią kairįjį kampą, rasime pirmąjį indeksą, turintį didžiausią likusių kvadratų skaičių. Taigi galime maišyti remSq[] masyvo reikšmę, kad rastume unikalų raktą visoms galimoms remSq[] masyvo reikšmėms.
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include
// Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.*; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int base = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Map<Integer Integer> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.containsKey(key)) return memo.get(key); int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = Arrays.copyOf(remSq b); int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo.put(key ans); return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; Arrays.fill(remSq a); Map<Integer Integer> memo = new HashMap<>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System.out.println(minCut(a b)); } }
# Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey(remSq b): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range(b): key += remSq[i] * base base = base * (b + 1) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil(remSq a b memo): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey(remSq b) if key in memo: return memo[key] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range(b): if remSq[i] > maxRemSq: maxRemSq = remSq[i] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0: return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq[:] ans = float('inf') # Find the ending point of min height while end < b: # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq or newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0: break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range(start end + 1): newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)) end += 1 memo[key] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut(a b): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b: return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [a] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) if __name__ == '__main__': # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print(minCut(a b))
// C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int baseVal = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * baseVal); baseVal = baseVal * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Dictionary<int int> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.ContainsKey(key)) return memo[key]; int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = (int[])remSq.Clone(); int ans = int.MaxValue; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.Min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) remSq[i] = a; Dictionary<int int> memo = new Dictionary<int int>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } static void Main() { int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console.WriteLine(minCut(a b)); } }
// JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey(remSq b) { let base = 1; let key = 0; for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey(remSq b); if (key in memo) return memo[key]; let maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq === 0) return 0; end = start; let newRemSq = remSq.slice(); let ans = Infinity; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut(a b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a === b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array(b).fill(a); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console.log(minCut(a b));
Išvestis
6
Laiko sudėtingumas: O(a^b) kiekvienam iš b stulpelių galime turėti a kvadratą.
Pagalbinė erdvė: O(a^b) dėl atmintinės, kurioje saugoma kiekviena unikali būsena.

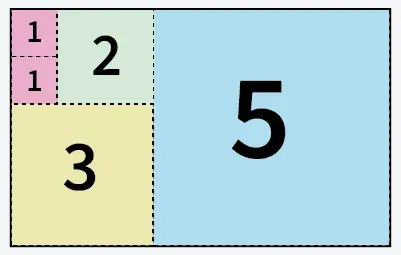 5 kvadratai, iškirpti iš 5 x 8 dydžio popieriaus
5 kvadratai, iškirpti iš 5 x 8 dydžio popieriaus 6 kvadratai, iškirpti iš 13 x 11 dydžio popieriaus
6 kvadratai, iškirpti iš 13 x 11 dydžio popieriaus 5 kvadratai, iškirpti iš 6 x 7 dydžio popieriaus
5 kvadratai, iškirpti iš 6 x 7 dydžio popieriaus