Minimax yra savotiškas atbulinės eigos algoritmas, kuris naudojamas priimant sprendimus ir žaidimo teorijoje, siekiant surasti optimalų žaidėjo judesį, darant prielaidą, kad jūsų priešininkas taip pat žaidžia optimaliai. Jis plačiai naudojamas dviejų žaidėjų ėjimo žaidimuose, tokiuose kaip Tic-Tac-Toe, Backgammon, Mancala, Chess ir kt.
Minimax du žaidėjai vadinami maksimizatoriumi ir minimizatoriumi. The maksimizatorius bando surinkti aukščiausią įmanomą balą minimizatorius bando elgtis priešingai ir gauti mažiausią įmanomą balą.
Kiekviena lentos būsena turi su ja susijusią vertę. Tam tikroje būsenoje, jei maksimizatorius turi pranašumą, lentos rezultatas bus teigiamas. Jei toje plokštės būsenoje minimizatorius turi pranašumą, jis paprastai turi neigiamą reikšmę. Lentos vertės apskaičiuojamos pagal euristiką, kuri yra unikali kiekvienam žaidimo tipui.
Pavyzdys:
Apsvarstykite žaidimą, kuriame yra 4 galutinės būsenos, o keliai pasiekti galutinę būseną yra nuo šaknų iki 4 tobulo dvejetainio medžio lapų, kaip parodyta žemiau. Tarkime, kad esate maksimizuojantis žaidėjas ir gaunate pirmąją galimybę judėti, t. y. esate šaknyje, o jūsų priešininkas kitame lygyje. Kokį judesį atliktumėte kaip maksimizuojantis žaidėjas, atsižvelgiant į tai, kad jūsų varžovas taip pat žaidžia optimaliai?
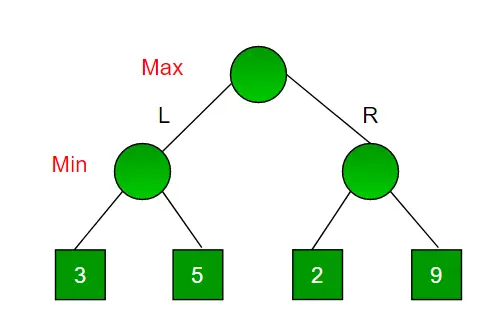
Kadangi tai yra atgaliniu keliu pagrįstas algoritmas, jis išbando visus įmanomus judesius, tada grįžta atgal ir priima sprendimą.
- Maksimalizatorius eina KAIRĖN: Dabar atėjo minimizatorių eilė. Minimalizatorius dabar turi pasirinkimą tarp 3 ir 5. Būdamas minimalizatoriumi, jis tikrai pasirinks mažiausiai iš abiejų, tai yra 3
- Maksimalizatorius eina į DEŠINĘ: dabar atėjo minizatorių eilė. Minimalizatorius dabar gali pasirinkti tarp 2 ir 9. Jis pasirinks 2, nes tai yra mažiausia iš dviejų reikšmių.
Būdami maksimizuotoju, pasirinktumėte didesnę reikšmę, kuri yra 3. Taigi optimalus maksimizatoriaus judėjimas yra eiti KAIRĖN, o optimali vertė yra 3.
Dabar žaidimo medis atrodo taip:

Aukščiau pateiktame medyje rodomi du galimi balai, kai maksimizatorius juda į kairę ir į dešinę.
Pastaba: nors dešiniajame pomedžio reikšmė yra 9, sumažinimo priemonė niekada to neparinks. Visada turime manyti, kad mūsų varžovas žaidžia optimaliai.
Žemiau pateikiamas to paties įgyvendinimas.
C++
dydžio latekso šriftas
// A simple C++ program to find> // maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is> // of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>bool> isMax,> >int> scores[],>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e> >// leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer,> >// find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> int> log2(>int> n)> {> >return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> scores[] = {3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23};> >int> n =>sizeof>(scores)/>sizeof>(scores[0]);> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >cout <<>'The optimal value is : '> << res << endl;> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Java
Vijay kino aktorius
// A simple java program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> import> java.io.*;> class> GFG {> > // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> >static> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>boolean> isMax,> >int> scores[],>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.max(minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2>,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2> +>1>,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.min(minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2>,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2> +>1>,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> >static> int> log2(>int> n)> {> return> (n==>1>)?>0> :>1> + log2(n/>2>);> }> // Driver code> >public> static> void> main (String[] args) {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> scores[] = {>3>,>5>,>2>,>9>,>12>,>5>,>23>,>23>};> >int> n = scores.length;> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(>0>,>0>,>true>, scores, h);> >System.out.println(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > >}> }> // This code is contributed by vt_m> |
>
>
C#
c programa stygų palyginimui
// A simple C# program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> using> System;> public> class> GFG> {> > // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> static> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>bool> isMax,> >int> []scores,>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.Max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.Min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> static> int> log2(>int> n)> {> >return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> // Driver code> static> public> void> Main ()> {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> []scores = {3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23};> >int> n = scores.Length;> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >Console.WriteLine(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > }> }> // This code is contributed by ajit.> |
>
>
Python3
# A simple Python3 program to find> # maximum score that> # maximizing player can get> import> math> def> minimax (curDepth, nodeIndex,> >maxTurn, scores,> >targetDepth):> ># base case : targetDepth reached> >if> (curDepth>=>=> targetDepth):> >return> scores[nodeIndex]> > >if> (maxTurn):> >return> max>(minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2>,> >False>, scores, targetDepth),> >minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2> +> 1>,> >False>, scores, targetDepth))> > >else>:> >return> min>(minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2>,> >True>, scores, targetDepth),> >minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2> +> 1>,> >True>, scores, targetDepth))> > # Driver code> scores>=> [>3>,>5>,>2>,>9>,>12>,>5>,>23>,>23>]> treeDepth>=> math.log(>len>(scores),>2>)> print>(>'The optimal value is : '>, end>=> '')> print>(minimax(>0>,>0>,>True>, scores, treeDepth))> # This code is contributed> # by rootshadow> |
>
>
java konvertuoti į eilutę
Javascript
> // Javascript program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> >function> minimax(depth, nodeIndex, isMax,> >scores, h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> > >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> > >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> > // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> >function> log2(n)> {> return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> > // Driver Code> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >let scores = [3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23];> >let n = scores.length;> >let h = log2(n);> >let res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >document.write(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > > > |
>
o ciklo java
>
Išvestis:
The optimal value is: 12>
Laiko sudėtingumas: O(b^d) b yra šakojimosi koeficientas, o d yra grafiko ar medžio gylio arba sluoksnio skaičius.
Erdvės sudėtingumas: O(bd), kur b yra šakojimosi koeficientas į d, yra didžiausias medžio gylis, panašus į DFS.
Šio straipsnio idėja yra pristatyti Minimax paprastu pavyzdžiu.
- Aukščiau pateiktame pavyzdyje žaidėjas turi tik du pasirinkimus. Apskritai, gali būti daugiau pasirinkimų. Tokiu atveju turime kartoti visus įmanomus judesius ir rasti maksimumą/minimumą. Pavyzdžiui, žaidime „Tic-Tac-Toe“ pirmasis žaidėjas gali atlikti 9 galimus ėjimus.
- Aukščiau pateiktame pavyzdyje balai (žaidimų medžio lapai) pateikiami mums. Įprastam žaidimui turime išvesti šias vertes
Netrukus apimsime Tic Tac Toe su Minimax algoritmu.
Prie šio straipsnio prisidėjo Akshay L. Aradhya.
