Šiame straipsnyje pamatysime įvairius būdus, kaip įrašyti į failą naudojant Java programavimo kalbą. Java FileWriter klasė java naudojama į failą įrašyti į simbolius orientuotus duomenis, nes ši klasė yra į simbolius orientuota klasė dėl to, kad ji naudojama tvarkyti java failus.
Yra daug Kaip įrašyti į failą Java kadangi yra daug klasių ir metodų, kurie gali pasiekti tokį tikslą:
- Naudojant writeString() metodas
- „FileWriter Class“ naudojimas
- Naudojant BufferedWriter klasę
- „FileOutputStream“ klasės naudojimas
1 būdas: naudokite writeString() metodą
Šį metodą palaiko Java 11 versija. Šis metodas gali būti keturių parametrų. Tai yra failo kelias, simbolių seka, simbolių rinkinys ir parinktys. Pirmieji du parametrai yra privalomi, kad šis metodas būtų įrašytas į failą. Ji rašo simbolius kaip failo turinį. Jis grąžina failo kelią ir gali pateikti keturių tipų išimtis. Geriau naudoti, kai failo turinys trumpas.
Pavyzdys: Tai rodo, kaip naudojamas writeString() Metodas, esantis failų klasėje, norint įrašyti duomenis į failą. Kita klasė, Path, naudojama priskirti failo pavadinimą su keliu, į kurį bus rašomas turinys. Failų klasė turi kitą metodą, pavadintą readString() nuskaityti bet kurio esamo failo, kuris naudojamas kode, turinį ir patikrinti, ar turinys tinkamai įrašytas faile.
Java
kaip išjungti kūrėjo režimą „Android“.
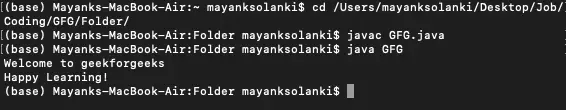
// Java Program to Write Into a File> // using writeString() Method> // Importing required classes> import> java.io.IOException;> import> java.nio.file.Files;> import> java.nio.file.Path;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >throws> IOException> >{> >// Assigning the content of the file> >String text> >=>'Welcome to geekforgeeks
Happy Learning!'>;> >// Defining the file name of the file> >Path fileName = Path.of(> >'/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'>);> >// Writing into the file> >Files.writeString(fileName, text);> >// Reading the content of the file> >String file_content = Files.readString(fileName);> >// Printing the content inside the file> >System.out.println(file_content);> >}> }> |
>
>Išvestis
Welcome to geekforgeeks Happy Learning!>
2 būdas: „FileWriter“ klasės naudojimas
Jei failo turinys yra trumpas, dar vienas geresnis pasirinkimas yra naudoti FileWriter klasę įrašymui į failą. Jis taip pat įrašo simbolių srautą kaip failo turinį, pavyzdžiui, writeString() metodas. Šios klasės konstruktorius apibrėžia numatytąją simbolių kodavimą ir numatytąjį buferio dydį baitais.
javascript skambinimo funkcija iš html
Toliau pateiktame pavyzdyje iliustruojamas „FileWriter“ klasės naudojimas turiniui įrašyti į failą. Norint įrašyti į failą, reikia sukurti FileWriter klasės objektą su failo pavadinimu. Toliau rašymo () metodas naudojamas teksto kintamojo reikšmei įrašyti faile. Jei rašant failą įvyksta kokia nors klaida, bus išmestas IOException, o klaidos pranešimas bus išspausdintas iš gaudymo bloko.
Pavyzdys:
Java
// Java Program to Write into a File> // using FileWriterClass> // Importing required classes> import> java.io.FileWriter;> import> java.io.IOException;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Content to be assigned to a file> >// Custom input just for illustration purposes> >String text> >=>'Computer Science Portal techcodeview.com'>;> >// Try block to check if exception occurs> >try> {> >// Create a FileWriter object> >// to write in the file> >FileWriter fWriter =>new> FileWriter(> >'/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'>);> >// Writing into file> >// Note: The content taken above inside the> >// string> >fWriter.write(text);> >// Printing the contents of a file> >System.out.println(text);> >// Closing the file writing connection> >fWriter.close();> >// Display message for successful execution of> >// program on the console> >System.out.println(> >'File is created successfully with the content.'>);> >}> >// Catch block to handle if exception occurs> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Print the exception> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >}> }> |
es5 prieš es6
>
>Išvestis
File is created successfully with the content.>

3 būdas: BufferedWriter klasės naudojimas
Jis naudojamas tekstui rašyti į simbolių išvesties srautą. Jis turi numatytąjį buferio dydį, tačiau galima priskirti didelį buferio dydį. Tai naudinga rašant simbolius, eilutes ir masyvus. Šią klasę geriau apvynioti bet kuria rašymo klase, kad būtų galima įrašyti duomenis į failą, jei nereikia skubios išvesties.
Pavyzdys:
Java
// Java Program to write into a File> // Using BufferedWriter Class> // Importing java input output libraries> import> java.io.BufferedWriter;> import> java.io.FileWriter;> import> java.io.IOException;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Assigning the file content> >// Note: Custom contents taken as input to> >// illustrate> >String text> >=>'Computer Science Portal techcodeview.com'>;> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Step 1: Create an object of BufferedWriter> >BufferedWriter f_writer> >=>new> BufferedWriter(>new> FileWriter(> >'/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'>));> >// Step 2: Write text(content) to file> >f_writer.write(text);> >// Step 3: Printing the content inside the file> >// on the terminal/CMD> >System.out.print(text);> >// Step 4: Display message showcasing> >// successful execution of the program> >System.out.print(> >'File is created successfully with the content.'>);> >// Step 5: Close the BufferedWriter object> >f_writer.close();> >}> >// Catch block to handle if exceptions occurs> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Print the exception on console> >// using getMessage() method> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Išvestis
25 iš 100
File is created successfully with the content.>

Šiame pavyzdyje parodytas BufferedWriter klasės naudojimas rašant į failą. Taip pat reikia sukurti „BufferedWriter“ klasės objektą, pvz., „FileWriter“, kad būtų galima įrašyti turinį į failą. Tačiau ši klasė palaiko didelį turinį, kurį galima įrašyti į failą naudojant didelį buferio dydį.
4 būdas: „FileOutputStream“ klasės naudojimas
Jis naudojamas neapdorotiems srauto duomenims įrašyti į failą. „FileWriter“ ir „BufferedWriter“ klasės naudojamos tik tekstui į failą įrašyti, tačiau dvejetainius duomenis galima įrašyti naudojant „FileOutputStream“ klasę.
Duomenų įrašymas į failą naudojant FileOutputStream klasė parodyta šiame pavyzdyje. Be to, norint įrašyti duomenis į failą, reikia sukurti klasės objektą su failo pavadinimu. Čia eilutės turinys konvertuojamas į baitų masyvą, kuris įrašomas į failą naudojant rašyti () metodas.
Pavyzdys:
Java
vlc atsisiųsti youtube vaizdo įrašus
// Java Program to Write into a File> // using FileOutputStream Class> // Importing java input output classes> import> java.io.FileOutputStream;> import> java.io.IOException;> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Assign the file content> >String fileContent =>'Welcome to geeksforgeeks'>;> >FileOutputStream outputStream =>null>;> >// Try block to check if exception occurs> >try> {> >// Step 1: Create an object of FileOutputStream> >outputStream =>new> FileOutputStream(>'file.txt'>);> >// Step 2: Store byte content from string> >byte>[] strToBytes = fileContent.getBytes();> >// Step 3: Write into the file> >outputStream.write(strToBytes);> >// Print the success message (Optional)> >System.out.print(> >'File is created successfully with the content.'>);> >}> >// Catch block to handle the exception> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Display the exception/s> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >// finally keyword is used with in try catch block> >// and this code will always execute whether> >// exception occurred or not> >finally> {> >// Step 4: Close the object> >if> (outputStream !=>null>) {> >// Note: Second try catch block ensures that> >// the file is closed even if an error> >// occurs> >try> {> >// Closing the file connections> >// if no exception has occurred> >outputStream.close();> >}> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Display exceptions if occurred> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >}> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Išvestis
File is created successfully with the content.>
