Sąrašai yra viena iš dažniausiai naudojamų Python duomenų struktūrų. Mes ir toliau naudojame sąrašus įvairiose programose – nuo paprastų iki sudėtingų problemų sprendimo. Python programoje sąrašai pakeičia masyvus tokiais pranašumais kaip:
- Dinamiškas dydis
- Gali saugoti skirtingų duomenų tipų elementus viename sąraše
Duomenis galime pasiekti tiesiog iš sąrašų pagal užsakymą; skirtingai nei rinkiniuose, duomenys bus netvarkomi. Norėdami pasiekti duomenis, galime naudoti kelis būdus, kaip kartoti kiekvieną sąrašo elementą. Ši pamoka apima visus būdus su pavyzdžiais.
1. Kilpos
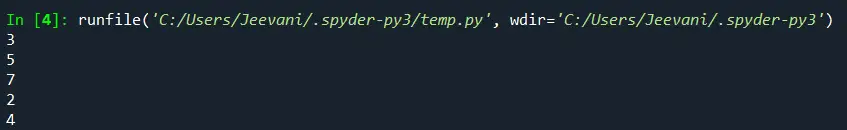
list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] count = 0 while (count <len(list1)): 1 print (list1 [count]) count="count" + < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>We created a list with a few elements. Initially, count = 0. We're printing the element at the 'count' index and incrementing the count in the while loop. When the count reaches the length of the list, the loop will be terminated, and all the elements will already be accessed.</p> <p> <strong>Mechanism:</strong> </p> <table class="table"> <tr> <td>count = 0</td> <td>list1 [0]</td> <td>3</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 1</td> <td>list1 [1]</td> <td>5</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 2</td> <td>list1 [2]</td> <td>7</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 3</td> <td>list1 [3]</td> <td>2</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 4</td> <td>list1 [4]</td> <td>4</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 5 = len (list1)</td> <td>-</td> <td>-</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <tr><td>Using for loop:</td> </tr></ul> <pre> list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] for i in list1: print (i) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-2.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>Using for-in, we accessed all the i's, the elements inside the list.</p> <ul> <tr><td>Using for and range:</td> </tr></ul> <pre> list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] length = len (list1) for i in range (0, len (list1)): print (list1 [i]) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-3.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>The range function helps the 'for' loop to iterate from 0 to the given list's length.</p> <p> <strong>Mechanism:</strong> </p> <table class="table"> <tr> <td>the range gives - 0</td> <td>list1 [0]</td> <td>3</td> </tr> <tr> <td>the range gives - 1</td> <td>list1 [1]</td> <td>5</td> </tr> <tr> <td>the range gives - 2</td> <td>list1 [2]</td> <td>7</td> </tr> <tr> <td>the range gives - 3</td> <td>list1 [3]</td> <td>2</td> </tr> <tr> <td>the range gives - 4</td> <td>list1 [4]</td> <td>4</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <li>The range function doesn't give the last element specified - len (list1) = 5 is not given.</li> </ul> <h2>2. Using List Comprehension</h2> <p>This is the simple and suggested way to iterate through a list in Python.</p> <p> <strong>Code:</strong> </p> <pre> list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] [print (i) for i in list1] print (' ') [print (list1 [i]) for i in range (0, len (list1))] print (' ') </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-4.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>We can use for loops inside a list comprehension. We used the same for loops we used in the above examples but inside a list in a single line. This way, we can reduce the length of the code and also list comprehension is a very subtle and efficient way to put loops in lists.</p> <h2>3. Using enumerate():</h2> <p>The enumerate function converts the given list into a list of tuples. Another important fact about this function is that it keeps count of the iterations. This is a built-in function in Python.</p> <p> <strong>Code:</strong> </p> <pre> list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] for i, j in enumerate (list1): print ('index = ', i, 'value: ', j) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-5.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <h2>4. Using lambda function and map():</h2> <p>These are anonymous functions. There is a function map () in Python that can accept a function as an argument, and it calls the function with every element in the iterable, and a new list with all the elements from the iterable will be returned.</p> <p> <strong>Code:</strong> </p> <pre> list1 = [3, 6, 1, 8, 7] result = list (map (lambda num: num, list1)) print (result) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-6.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>The lambda num: num is given as an input to the map function along with the list. The function will take every single element in the list, accept it, and then return it. The map () function will pass the list elements one by one to the lambda function to return the elements.</p> <h2>What if we want to Iterate Multi-dimensional Lists?</h2> <p>There is an inbuilt module in Python designed to perform operations on multi-dimensional lists.</p> <p> <strong>1. To get numpy:</strong> </p> <p>Check if Python and pip are installed by opening the cmd via search and typing the commands:</p> <p> <strong>Python -version</strong> </p> <p> <strong>Pip --version</strong> </p> <p>If both Python and PIP are present in our system, it is now time to install our library:</p> <p> <strong>2. Open cmd from the start menu</strong> </p> <p> <strong>3. Type the command</strong> </p> <h3>pip install numpy</h3> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p>All the library packages, data, and sub-packages will be installed one after the other.</p> <p> <strong>Code:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy list1 = numpy. arange (9) list1 = list1. reshape (3, 3) for x in numpy. nditer (list1): print (x) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-7.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>We imported the numpy module. Using the arrange method, we created an array with 9 elements. We accessed the list by reshaping it to 3 * 3 (rows * columns) using the reshape. Using the nditer function, we printed each element in the list.</p> <hr></len(list1)):>
Išvestis:

Supratimas:
Naudodami for-in pasiekėme visus i, sąrašo elementus.
list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] length = len (list1) for i in range (0, len (list1)): print (list1 [i])
Išvestis:

Supratimas:
Diapazono funkcija padeda „for“ kilpai kartoti nuo 0 iki nurodyto sąrašo ilgio.
Salman Khan amžius
Mechanizmas:
| diapazonas suteikia - 0 | 1 lapas [0] | 3 |
| diapazonas suteikia - 1 | 1 lapas [1] | 5 |
| diapazonas suteikia - 2 | 1 lapas [2] | 7 |
| diapazonas suteikia - 3 | 1 lapas [3] | 2 |
| diapazonas suteikia - 4 | 1 lapas [4] | 4 |
- Diapazono funkcija nepateikia paskutinio nurodyto elemento – len (list1) = 5 nenurodytas.
2. Sąrašo supratimo naudojimas
Tai paprastas ir siūlomas būdas kartoti sąrašą Python.
Kodas:
list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] [print (i) for i in list1] print (' ') [print (list1 [i]) for i in range (0, len (list1))] print (' ')
Išvestis:

Supratimas:
registro perdavimo logika
Sąrašo supratimo viduje galime naudoti kilpas. Tą patį naudojome kilpoms, kurias naudojome aukščiau pateiktuose pavyzdžiuose, bet sąraše vienoje eilutėje. Tokiu būdu galime sumažinti kodo ilgį, o sąrašo supratimas yra labai subtilus ir efektyvus būdas įtraukti kilpas į sąrašus.
3. Naudojant enumerate():
Surašymo funkcija paverčia pateiktą sąrašą į eilučių sąrašą. Kitas svarbus šios funkcijos faktas yra tai, kad ji nuolat skaičiuoja iteracijas. Tai yra Python integruota funkcija.
Kodas:
list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] for i, j in enumerate (list1): print ('index = ', i, 'value: ', j)
Išvestis:

4. Naudojant lambda funkciją ir žemėlapį():
Tai anoniminės funkcijos. Python yra funkcijų žemėlapis (), kuris gali priimti funkciją kaip argumentą ir iškviečia funkciją su kiekvienu iterable elementu, ir bus grąžintas naujas sąrašas su visais iterable elementais.
Kodas:
list1 = [3, 6, 1, 8, 7] result = list (map (lambda num: num, list1)) print (result)
Išvestis:

Supratimas:
Lambda skaičius: skaičius pateikiamas kaip žemėlapio funkcijos įvestis kartu su sąrašu. Funkcija paims kiekvieną sąrašo elementą, priims jį ir grąžins. Žemėlapio () funkcija perduos sąrašo elementus po vieną lambda funkcijai, kad grąžintų elementus.
Ką daryti, jei norime kartoti daugiamačius sąrašus?
Python yra integruotas modulis, skirtas atlikti operacijas su daugiamačiais sąrašais.
1. Jei norite nutirpti:
Patikrinkite, ar Python ir pip yra įdiegti, atidarydami cmd per paiešką ir įvesdami komandas:
lapė prieš vilką
Python versija
Pip -- versija
Jei mūsų sistemoje yra ir Python, ir PIP, dabar laikas įdiegti mūsų biblioteką:
2. Atidarykite cmd iš pradžios meniu
3. Įveskite komandą
pip install numpy
Visi bibliotekos paketai, duomenys ir antriniai paketai bus įdiegti vienas po kito.
Kodas:
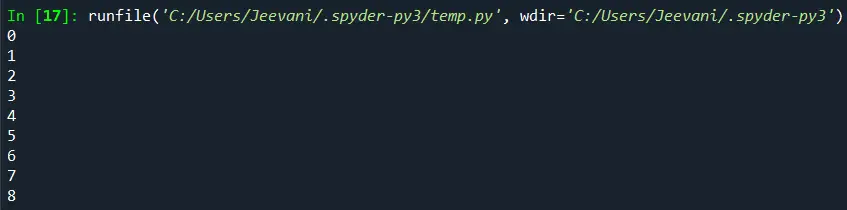
import numpy list1 = numpy. arange (9) list1 = list1. reshape (3, 3) for x in numpy. nditer (list1): print (x)
Išvestis:
Supratimas:
Mes importavome numpy modulį. Naudodami išdėstymo metodą sukūrėme masyvą su 9 elementais. Sąrašą pasiekėme pakeisdami jį į 3 * 3 (eilutės * stulpeliai) naudodami pertvarkymą. Naudodami funkciją nditer, išspausdinome kiekvieną sąrašo elementą.
