Kas yra Hamiltono ciklas?
Hamiltono ciklas arba grandinė grafike G yra ciklas, kuris aplanko kiekvieną viršūnę G lygiai vieną kartą ir grįžta į pradinę viršūnę.
- Jei grafike yra Hamiltono ciklas, jis vadinamas Hamiltono grafikas kitaip yra ne Hamiltono .
- Hamiltono ciklo radimas grafike yra gerai žinomas NP-visiška problema , o tai reiškia, kad nėra žinomo veiksmingo algoritmo, kuris jį išspręstų visų tipų grafikuose. Tačiau tai gali būti išspręsta mažiems ar specifiniams grafikų tipams.
Hamiltono ciklo problema turi praktinį pritaikymą įvairiose srityse, pvz logistika, tinklų projektavimas ir informatika .
Kas yra Hamiltono kelias?
Hamiltono kelias grafike G yra kelias, kuris kiekvieną G viršūnę aplanko tiksliai vieną kartą ir Hamiltono kelias neturi grįžti į pradinę viršūnę. Tai atviras kelias.
- Panašus į Hamiltono ciklas problema, rasti a Hamiltono kelias bendrame grafike taip pat yra NP pilnas ir gali būti sudėtinga. Tačiau tai dažnai yra lengvesnė problema nei rasti Hamiltono ciklą.
- Hamiltono takai turi pritaikymų įvairiose srityse, pvz optimalių maršrutų radimas transporto tinklų, grandinių projektavimo ir grafų teorijos tyrimuose .
Problemų pareiškimas: Pateikus neorientuotą grafą, užduotis yra nustatyti, ar grafe yra Hamiltono ciklas, ar ne. Jei jame yra, tada išspausdinamas kelias.
Pavyzdys:
Rekomenduojama: išspręskite PRAKTIKA pirma, prieš pereinant prie sprendimo.Įvestis: grafikas[][] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0},{1, 0, 1, 1, 1},{0, 1, 0, 0, 1},{1, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 1, 1, 1, 0}}
Įvesties grafikas[][]
apibrėžti kompiuterįIšvestis: 0, 1, 2, 4, 3, 0}.
Įvestis: grafikas[][] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0},{1, 0, 1, 1, 1},{0, 1, 0, 0, 1},{1, 1, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 1, 0, 0}}
Įvesties grafikas[][]
Išvestis: Sprendimas neegzistuoja
Naivus algoritmas : Šią problemą galima išspręsti naudojant toliau pateiktą idėją:
Sugeneruokite visas įmanomas viršūnių konfigūracijas ir išspausdinkite konfigūraciją, atitinkančią nurodytus apribojimus. Bus n! (n faktorinės) konfigūracijos. Taigi bendras šio požiūrio laiko sudėtingumas bus O (N!).
Hamiltono ciklo naudojimas Atgalinis algoritmas :
Sukurkite tuščią kelio masyvą ir pridėkite viršūnę 0 prie jo. Pridėkite kitas viršūnes, pradedant nuo viršūnės 1 . Prieš įtraukdami viršūnę patikrinkite, ar ji yra greta anksčiau pridėtos viršūnės ir dar nėra pridėta. Jei randame tokią viršūnę, ją pridedame kaip sprendimo dalį. Jei nerandame viršūnės, grįžtame klaidinga .
Iliustracijos:
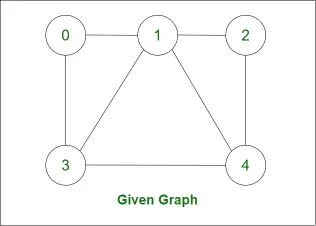
Sužinokime Hamiltono ciklą tokiam grafikui:
- Pradėkite nuo mazgo 0.
- Norėdami rasti Hamiltono kelią, taikykite DFS.
- Kai pasiekiamas bazinis dydis (t. y. bendras pervažiuoto mazgo skaičius == V (bendra viršūnė) ):
- Patikrinkite, ar dabartinis mazgas yra pradinio mazgo kaimynas.
- Kaip mazgas 2 ir mazgas 0 nėra vienas kito kaimynai, todėl grįžkite iš jo.
Pradedant nuo 0 mazgo, iškviečiančio DFS
- Kadangi ciklas nerastas kelyje {0, 3, 1, 4, 2}. Taigi, grįžkite iš 2 mazgo, 4 mazgo.
- Dabar ištirkite kitą 1 mazgo (ty 2 mazgo) parinktį.
- Kai jis vėl pasiekia bazinę būklę, patikrinkite Hamiltono ciklą
- Kadangi 4 mazgas nėra 0 mazgo kaimynas, ciklas vėl nerastas, tada grįžkite.
- Grįžimas iš 4 mazgo, 2 mazgo, 1 mazgo.
- Dabar ištirkite kitas 3 mazgo parinktis.
Hamiltono ciklas
- Hamiltono kelyje 0,3,4,2,1,0} gauname ciklą, nes 1 mazgas yra 0 mazgo kaimynas.
- Taigi atspausdinkite šį ciklinį kelią.
- Tai mūsų Hamiltono ciklas.
Toliau pateikiamas „Backtracking“ diegimas, skirtas Hamiltono ciklui rasti:
C++ /* C++ program for solution of Hamiltonian Cycle problem using backtracking */ #include using namespace std; // Number of vertices in the graph #define V 5 void printSolution(int path[]); /* A utility function to check if the vertex v can be added at index 'pos' in the Hamiltonian Cycle constructed so far (stored in 'path[]') */ bool isSafe(int v, bool graph[V][V], int path[], int pos) { /* Check if this vertex is an adjacent vertex of the previously added vertex. */ if (graph [path[pos - 1]][ v ] == 0) return false; /* Check if the vertex has already been included. This step can be optimized by creating an array of size V */ for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) if (path[i] == v) return false; return true; } /* A recursive utility function to solve hamiltonian cycle problem */ bool hamCycleUtil(bool graph[V][V], int path[], int pos) { /* base case: If all vertices are included in Hamiltonian Cycle */ if (pos == V) { // And if there is an edge from the // last included vertex to the first vertex if (graph[path[pos - 1]][path[0]] == 1) return true; else return false; } // Try different vertices as a next candidate // in Hamiltonian Cycle. We don't try for 0 as // we included 0 as starting point in hamCycle() for (int v = 1; v < V; v++) { /* Check if this vertex can be added // to Hamiltonian Cycle */ if (isSafe(v, graph, path, pos)) { path[pos] = v; /* recur to construct rest of the path */ if (hamCycleUtil (graph, path, pos + 1) == true) return true; /* If adding vertex v doesn't lead to a solution, then remove it */ path[pos] = -1; } } /* If no vertex can be added to Hamiltonian Cycle constructed so far, then return false */ return false; } /* This function solves the Hamiltonian Cycle problem using Backtracking. It mainly uses hamCycleUtil() to solve the problem. It returns false if there is no Hamiltonian Cycle possible, otherwise return true and prints the path. Please note that there may be more than one solutions, this function prints one of the feasible solutions. */ bool hamCycle(bool graph[V][V]) { int *path = new int[V]; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) path[i] = -1; /* Let us put vertex 0 as the first vertex in the path. If there is a Hamiltonian Cycle, then the path can be started from any point of the cycle as the graph is undirected */ path[0] = 0; if (hamCycleUtil(graph, path, 1) == false ) { cout << '
Solution does not exist'; return false; } printSolution(path); return true; } /* A utility function to print solution */ void printSolution(int path[]) { cout << 'Solution Exists:' ' Following is one Hamiltonian Cycle
'; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) cout << path[i] << ' '; // Let us print the first vertex again // to show the complete cycle cout << path[0] << ' '; cout << endl; } // Driver Code int main() { /* Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3)-------(4) */ bool graph1[V][V] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 1, 1, 1, 0}}; // Print the solution hamCycle(graph1); /* Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3) (4) */ bool graph2[V][V] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 1, 0, 0}}; // Print the solution hamCycle(graph2); return 0; } // This is code is contributed by rathbhupendra> C++ #include using namespace std; int main() { cout << 'GFG!'; return 0; }> C /* C program for solution of Hamiltonian Cycle problem using backtracking */ #include // Number of vertices in the graph #define V 5 void printSolution(int path[]); /* A utility function to check if the vertex v can be added at index 'pos' in the Hamiltonian Cycle constructed so far (stored in 'path[]') */ int isSafe(int v, int graph[V][V], int path[], int pos) { /* Check if this vertex is an adjacent vertex of the previously added vertex. */ if (graph [ path[pos-1] ][ v ] == 0) return 0; /* Check if the vertex has already been included. This step can be optimized by creating an array of size V */ for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) if (path[i] == v) return 0; return 1; } /* A recursive utility function to solve hamiltonian cycle problem */ int hamCycleUtil(int graph[V][V], int path[], int pos) { /* base case: If all vertices are included in Hamiltonian Cycle */ if (pos == V) { // And if there is an edge from the last included vertex to the // first vertex if ( graph[ path[pos-1] ][ path[0] ] == 1 ) return 1; else return 0; } // Try different vertices as a next candidate in Hamiltonian Cycle. // We don't try for 0 as we included 0 as starting point in hamCycle() for (int v = 1; v < V; v++) { /* Check if this vertex can be added to Hamiltonian Cycle */ if (isSafe(v, graph, path, pos)) { path[pos] = v; /* recur to construct rest of the path */ if (hamCycleUtil (graph, path, pos+1) == 1) return 1; /* If adding vertex v doesn't lead to a solution, then remove it */ path[pos] = -1; } } /* If no vertex can be added to Hamiltonian Cycle constructed so far, then return false */ return 0; } /* This function solves the Hamiltonian Cycle problem using Backtracking. It mainly uses hamCycleUtil() to solve the problem. It returns false if there is no Hamiltonian Cycle possible, otherwise return true and prints the path. Please note that there may be more than one solutions, this function prints one of the feasible solutions. */ int hamCycle(int graph[V][V]) { int path[V]; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) path[i] = -1; /* Let us put vertex 0 as the first vertex in the path. If there is a Hamiltonian Cycle, then the path can be started from any point of the cycle as the graph is undirected */ path[0] = 0; if ( hamCycleUtil(graph, path, 1) == 0 ) { printf('
Solution does not exist'); return 0; } printSolution(path); return 1; } /* A utility function to print solution */ void printSolution(int path[]) { printf ('Solution Exists:' ' Following is one Hamiltonian Cycle
'); for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) printf(' %d ', path[i]); // Let us print the first vertex again to show the complete cycle printf(' %d ', path[0]); printf('
'); } // driver program to test above function int main() { /* Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3)-------(4) */ int graph1[V][V] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 1, 1, 1, 0}, }; // Print the solution hamCycle(graph1); /* Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3) (4) */ int graph2[V][V] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, }; // Print the solution hamCycle(graph2); return 0; }> Java /* Java program for solution of Hamiltonian Cycle problem using backtracking */ class HamiltonianCycle { final int V = 5; int path[]; /* A utility function to check if the vertex v can be added at index 'pos'in the Hamiltonian Cycle constructed so far (stored in 'path[]') */ boolean isSafe(int v, int graph[][], int path[], int pos) { /* Check if this vertex is an adjacent vertex of the previously added vertex. */ if (graph[path[pos - 1]][v] == 0) return false; /* Check if the vertex has already been included. This step can be optimized by creating an array of size V */ for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) if (path[i] == v) return false; return true; } /* A recursive utility function to solve hamiltonian cycle problem */ boolean hamCycleUtil(int graph[][], int path[], int pos) { /* base case: If all vertices are included in Hamiltonian Cycle */ if (pos == V) { // And if there is an edge from the last included // vertex to the first vertex if (graph[path[pos - 1]][path[0]] == 1) return true; else return false; } // Try different vertices as a next candidate in // Hamiltonian Cycle. We don't try for 0 as we // included 0 as starting point in hamCycle() for (int v = 1; v < V; v++) { /* Check if this vertex can be added to Hamiltonian Cycle */ if (isSafe(v, graph, path, pos)) { path[pos] = v; /* recur to construct rest of the path */ if (hamCycleUtil(graph, path, pos + 1) == true) return true; /* If adding vertex v doesn't lead to a solution, then remove it */ path[pos] = -1; } } /* If no vertex can be added to Hamiltonian Cycle constructed so far, then return false */ return false; } /* This function solves the Hamiltonian Cycle problem using Backtracking. It mainly uses hamCycleUtil() to solve the problem. It returns false if there is no Hamiltonian Cycle possible, otherwise return true and prints the path. Please note that there may be more than one solutions, this function prints one of the feasible solutions. */ int hamCycle(int graph[][]) { path = new int[V]; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) path[i] = -1; /* Let us put vertex 0 as the first vertex in the path. If there is a Hamiltonian Cycle, then the path can be started from any point of the cycle as the graph is undirected */ path[0] = 0; if (hamCycleUtil(graph, path, 1) == false) { System.out.println('
Solution does not exist'); return 0; } printSolution(path); return 1; } /* A utility function to print solution */ void printSolution(int path[]) { System.out.println('Solution Exists: Following' + ' is one Hamiltonian Cycle'); for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) System.out.print(' ' + path[i] + ' '); // Let us print the first vertex again to show the // complete cycle System.out.println(' ' + path[0] + ' '); } // driver program to test above function public static void main(String args[]) { HamiltonianCycle hamiltonian = new HamiltonianCycle(); /* Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3)-------(4) */ int graph1[][] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 1, 1, 1, 0}, }; // Print the solution hamiltonian.hamCycle(graph1); /* Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3) (4) */ int graph2[][] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, }; // Print the solution hamiltonian.hamCycle(graph2); } } // This code is contributed by Abhishek Shankhadhar> Python # Python program for solution of # hamiltonian cycle problem class Graph(): def __init__(self, vertices): self.graph = [[0 for column in range(vertices)] for row in range(vertices)] self.V = vertices ''' Check if this vertex is an adjacent vertex of the previously added vertex and is not included in the path earlier ''' def isSafe(self, v, pos, path): # Check if current vertex and last vertex # in path are adjacent if self.graph[ path[pos-1] ][v] == 0: return False # Check if current vertex not already in path for vertex in path: if vertex == v: return False return True # A recursive utility function to solve # hamiltonian cycle problem def hamCycleUtil(self, path, pos): # base case: if all vertices are # included in the path if pos == self.V: # Last vertex must be adjacent to the # first vertex in path to make a cycle if self.graph[ path[pos-1] ][ path[0] ] == 1: return True else: return False # Try different vertices as a next candidate # in Hamiltonian Cycle. We don't try for 0 as # we included 0 as starting point in hamCycle() for v in range(1,self.V): if self.isSafe(v, pos, path) == True: path[pos] = v if self.hamCycleUtil(path, pos+1) == True: return True # Remove current vertex if it doesn't # lead to a solution path[pos] = -1 return False def hamCycle(self): path = [-1] * self.V ''' Let us put vertex 0 as the first vertex in the path. If there is a Hamiltonian Cycle, then the path can be started from any point of the cycle as the graph is undirected ''' path[0] = 0 if self.hamCycleUtil(path,1) == False: print ('Solution does not exist
') return False self.printSolution(path) return True def printSolution(self, path): print ('Solution Exists: Following', 'is one Hamiltonian Cycle') for vertex in path: print (vertex ) # Driver Code ''' Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3)-------(4) ''' g1 = Graph(5) g1.graph = [ [0, 1, 0, 1, 0], [1, 0, 1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 0, 0, 1,],[1, 1, 0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 1, 1, 0], ] # Print the solution g1.hamCycle(); ''' Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3) (4) ''' g2 = Graph(5) g2.graph = [ [0, 1, 0, 1, 0], [1, 0, 1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 0, 0, 1,], [1, 1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 1, 0, 0], ] # Print the solution g2.hamCycle(); # This code is contributed by Divyanshu Mehta> C# // C# program for solution of Hamiltonian // Cycle problem using backtracking using System; public class HamiltonianCycle { readonly int V = 5; int []path; /* A utility function to check if the vertex v can be added at index 'pos'in the Hamiltonian Cycle constructed so far (stored in 'path[]') */ bool isSafe(int v, int [,]graph, int []path, int pos) { /* Check if this vertex is an adjacent vertex of the previously added vertex. */ if (graph[path[pos - 1], v] == 0) return false; /* Check if the vertex has already been included. This step can be optimized by creating an array of size V */ for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) if (path[i] == v) return false; return true; } /* A recursive utility function to solve hamiltonian cycle problem */ bool hamCycleUtil(int [,]graph, int []path, int pos) { /* base case: If all vertices are included in Hamiltonian Cycle */ if (pos == V) { // And if there is an edge from the last included // vertex to the first vertex if (graph[path[pos - 1],path[0]] == 1) return true; else return false; } // Try different vertices as a next candidate in // Hamiltonian Cycle. We don't try for 0 as we // included 0 as starting point in hamCycle() for (int v = 1; v < V; v++) { /* Check if this vertex can be added to Hamiltonian Cycle */ if (isSafe(v, graph, path, pos)) { path[pos] = v; /* recur to construct rest of the path */ if (hamCycleUtil(graph, path, pos + 1) == true) return true; /* If adding vertex v doesn't lead to a solution, then remove it */ path[pos] = -1; } } /* If no vertex can be added to Hamiltonian Cycle constructed so far, then return false */ return false; } /* This function solves the Hamiltonian Cycle problem using Backtracking. It mainly uses hamCycleUtil() to solve the problem. It returns false if there is no Hamiltonian Cycle possible, otherwise return true and prints the path. Please note that there may be more than one solutions, this function prints one of the feasible solutions. */ int hamCycle(int [,]graph) { path = new int[V]; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) path[i] = -1; /* Let us put vertex 0 as the first vertex in the path. If there is a Hamiltonian Cycle, then the path can be started from any point of the cycle as the graph is undirected */ path[0] = 0; if (hamCycleUtil(graph, path, 1) == false) { Console.WriteLine('
Solution does not exist'); return 0; } printSolution(path); return 1; } /* A utility function to print solution */ void printSolution(int []path) { Console.WriteLine('Solution Exists: Following' + ' is one Hamiltonian Cycle'); for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) Console.Write(' ' + path[i] + ' '); // Let us print the first vertex again // to show the complete cycle Console.WriteLine(' ' + path[0] + ' '); } // Driver code public static void Main(String []args) { HamiltonianCycle hamiltonian = new HamiltonianCycle(); /* Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3)-------(4) */ int [,]graph1= {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 1, 1, 1, 0}, }; // Print the solution hamiltonian.hamCycle(graph1); /* Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3) (4) */ int [,]graph2 = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, }; // Print the solution hamiltonian.hamCycle(graph2); } } // This code contributed by Rajput-Ji> Javascript >>PHP>>
Išvestis Laiko sudėtingumas: O(N!), kur N yra viršūnių skaičius.
Pagalbinė erdvė: O(1), nes nenaudojama papildomos vietos. Pastaba: Aukščiau pateiktas kodas visada spausdina ciklą, prasidedantį nuo 0 . Pradinis taškas neturėtų būti svarbus, nes ciklą galima pradėti nuo bet kurio taško. Jei norite pakeisti pradžios tašką, turėtumėte atlikti du aukščiau pateikto kodo pakeitimus.
Keisti kelią[0] = 0; į kelias[0] = s ; kur s yra tavo naujiena atspirties taškas . Taip pat pakeiskite kilpą (int v = 1; v